Notizie per Categorie
Articoli Recenti
- [Launched] Generally Available: New Microsoft Dev Box Regional Availability 1 Aprile 2025
- [In preview] Public Preview: CNI Overlay for Application Gateway for Containers and AGIC 1 Aprile 2025
- Transforming public sector security operations in the AI era 1 Aprile 2025
- [In preview] Public Preview: Azure Front Door Custom Cipher Suite 1 Aprile 2025
- [Launched] Public Preview: Azure Monitor Application Insights Auto-Instrumentation for Java and Node Microservices on AKS 1 Aprile 2025
- Retirement: Log Analytics Beta API to Be Retired on March 31, 2026 1 Aprile 2025
- Retirement: Log Analytics Batch API to Be Retired on March 31, 2028 1 Aprile 2025
- [In preview] Public Preview: ExpressRoute Resiliency Enhancements 1 Aprile 2025
- Retirement: Azure Machine Learning SDK v1 Will Be Retired on March 31, 2025 – Transition to Machine Learning SDK v2 31 Marzo 2025
- Retirement: Cloud Services (Extended Support) to Be Retired on March 31, 2027 31 Marzo 2025
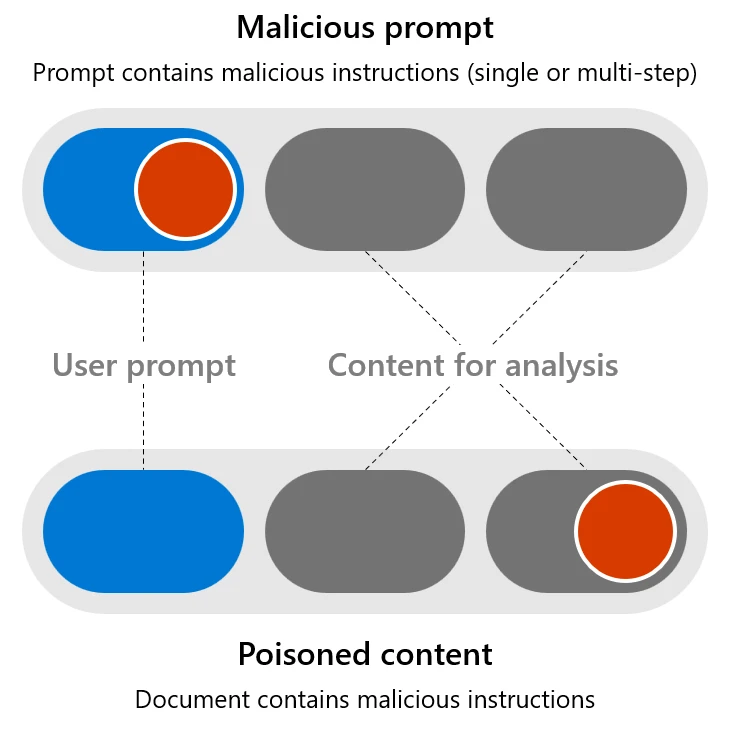
As we continue to integrate generative AI into our daily lives, it’s important to understand the potential harms that can arise from its use. Our ongoing commitment to advance safe, secure, and trustworthy AI includes transparency about the capabilities and limitations of large language models (LLMs). We prioritize[…]
Read More
Today we launched the 2024 release wave 1 for Microsoft Dynamics 365 and Microsoft Power Platform, a rollout of new features and enhanced capabilities slated for release between April and September 2024. These updates include new Microsoft Copilot capabilities across Dynamics 365 and Microsoft Power Platform—as well as role-based extensions of Copilot[…]
Read More
The security of your organization directly correlates with your ability to transform and achieve your business objectives. Microsoft can help you make that happen, with our powerful combination of large-scale data and threat intelligence, end-to-end protection, and responsible AI. Recently at Microsoft Secure, we shared our latest innovations[…]
Read More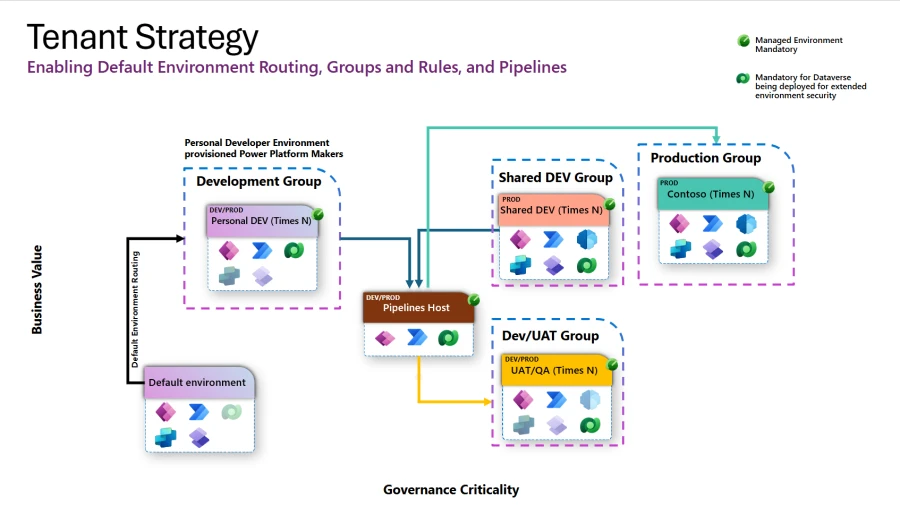
Preview Microsoft Power Platform environment groups and rules As organizations expand their Microsoft Power Platform footprint to meet the needs of their users for application modernization and the inclusion of Microsoft Copilot, administrators can utilize premium features such as managed environments to govern at-scale quickly and easily, while[…]
Read More
Today, I am excited to announce the public preview of our unified security operations platform. When we announced a limited preview in November 2023, it was one of the first security operations center platforms that brought together the full capabilities of an industry-leading cloud-native security information and event[…]
Read More
We know managing privacy is harder than ever. The increasing complexity of regulatory requirements and constantly changing regulations make day-to-day privacy management a challenge. Manual, inefficient processes and inflexible tools can make it difficult for organizations to know where data is located and how it’s being used. The[…]
Read More
Are you curious about some of the innovations that make Microsoft Power Platform a game-changer for businesses of all sizes and industries? Hear directly from attendees of the Microsoft Power Platform Conference who shared their insights and experiences. From generative AI, to how the out-of-box governance and security[…]
Read More
The past 12 months marked the beginning of the era of AI. In March 2023, Microsoft took the lead in AI transformation with the introduction of Microsoft Copilot, which has since been deeply integrated in the company’s portfolio—including Microsoft Power Platform—with generative AI transforming how organizations work, collaborate,[…]
Read More
We live in a world where data is constantly multiplying. According to IDC, the global datasphere, which is the amount of data created, captured, or replicated, will double every four years.1 As AI becomes more prevalent in various domains, organizations face the challenge of securing their growing data[…]
Read More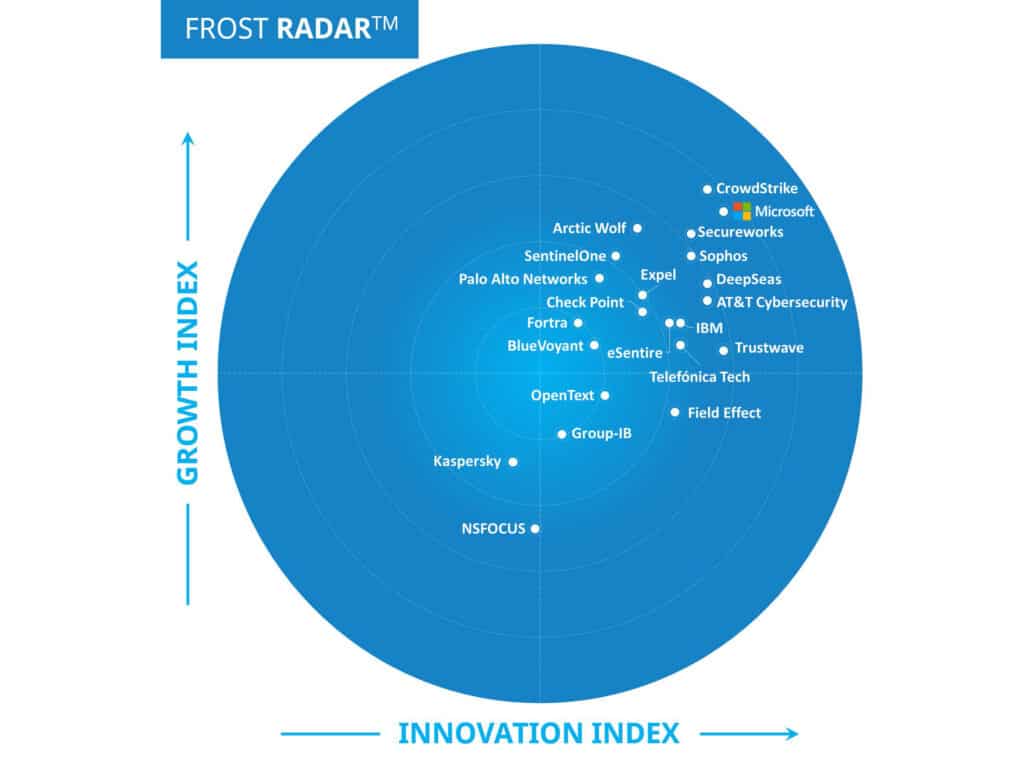
We are excited to share that Microsoft has been named a Leader by Frost & Sullivan in the Frost Radar™: Managed Detection and Response, 2024, leading in innovation and among the top two in growth. Frost & Sullivan highlighted Microsoft Defender Experts for XDR as a key component[…]
Read More