Notizie per Categorie
Articoli Recenti
- Explore practical best practices to secure your data with Microsoft Purview 25 Aprile 2025
- New whitepaper outlines the taxonomy of failure modes in AI agents 24 Aprile 2025
- Understanding the threat landscape for Kubernetes and containerized assets 23 Aprile 2025
- [Launched] Generally Available: Instance Mix for Virtual Machine Scale Sets 22 Aprile 2025
- Microsoft’s AI vision shines at MWC 2025 in Barcelona 22 Aprile 2025
- [Launched] Generally Available: Announcing the Next generation Azure Data Box Devices 22 Aprile 2025
- [Launched] Generally Available: Cross-Region Data Transfer Capability in Azure Data Box Devices 21 Aprile 2025
- [Launched] Generally Available: Azure Ultra Disk Storage is now available in Spain Central 21 Aprile 2025
- [Launched] Generally Available: Azure Firewall resource specific log tables get Azure Monitor Basic plan support 21 Aprile 2025
- Hannover Messe 2025: Microsoft puts industrial AI to work 21 Aprile 2025
How implementing a trust fabric strengthens identity and network
The identity security landscape is transforming rapidly. Every digital experience and interaction is an opportunity for people to connect, share, and collaborate. But first, we need to know we can trust those digital experiences and interactions. Customers note a massive rise in the sheer number of identities they need to enable, connect, and protect. These include not only human identities like employees, partners, and customers, but also non-human or machine identities—which outnumber humans and continue to grow exponentially. All these identities come with unique risks, but they’re central to business organizations’ need to create effective, seamless connections—both for people and their apps, data, and networks.
At the same time, the number and complexity of cyberthreats continues to grow. This makes the challenge of securing human and non-human identities urgent and critical. Phishing, ransomware, and both internal and external threats have increased significantly. And threat actors are quickly exploiting newer technologies like generative AI to create and scale their attacks.
In the face of these challenges and the acceleration of AI opportunities and risks, what we think of as traditional identity and access management is no longer enough. We need to ensure the right people, machines, and software components get access to the right resources at the right time, while keeping out any bad actors or cyberthreats. We need to be able to secure access for any trustworthy identity, anywhere, to any app, resource, or AI tool at any time.
We take these challenges very seriously. Our teams have been hard at work, listening to customers and analyzing data—and utilizing the modern technologies enabled by AI—to stay ahead of threats and step up our defenses. This new era demands a comprehensive, adaptive, real-time approach to securing access.
At Microsoft, we call this approach the trust fabric.
Think global, act local
In years past, the firewall was the clear perimeter of network protection for customers. Then the buzz was “identity is the new perimeter” as people began to work from home and do their work on personal devices. And recently, the term “identity fabric,” coined by industry analysts in 2023, has been used by many to describe identity and access management (IAM) concepts and capabilities. But the move from a network control plane to an identity-centric control plane is just the beginning. Flexible work models, cloud apps and services, digitized business processes, AI, and more can no longer be managed by a single identity control plane. It would slow down the speed of business and become a choke point.
Instead, to meet the needs of our ever-expanding digital estate, we need a “think global, act local” approach. A combination of centralized decisions and policies would determine what is allowed to happen at the edges—the points of interaction—with multiple, distributed control planes at both the identity and network levels. In addition to identity, the network and endpoints are equally critical signals. The controls and policies should be unified with identity to reduce complexity and gaps. This is the distinction between identity fabric and the next step: trust fabric. In this era of ubiquitous, decentralized computing, data centers can serve as the intelligent cloud, facilitating interaction with smart devices and services on the intelligent edge. This decentralized identity model can also help achieve the speed required to authorize so many devices and services at scale. The vision for how to conceptually architect and move forward with this comprehensive defense-in-depth cybersecurity strategy is the same as a trust fabric. As such, Microsoft’s trust fabric concept expands beyond traditional IAM to weave together comprehensive, unified identity, network access, and endpoint controls.

Figure 1. Identity security has evolved from directory services and firewalls to cloud-centered identity services to today’s decentralized trust fabric approach.
Zero Trust and a trust fabric
Zero Trust is the term for an evolving set of cybersecurity paradigms that move cybersecurity defenses from static, network-based perimeters to focus on users, assets, and resources. The concept of Zero Trust has been around in cybersecurity for some time and is increasingly important as enterprise infrastructure continues to become decentralized and increases in complexity. In 2020, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) released a security-wide framework or model of Zero Trust based on three core principles: Verify explicitly, ensure least-privileged access, and assume breach. The Zero Trust principles are foundational to how organizations should architect a trust fabric, and instructional for how to build technology to bring the trust fabric to life.
A Zero Trust strategy is a proactive, integrated approach to security across all layers of the digital estate. A modern comprehensive implementation of Zero Trust protects assets wherever they are. It includes solutions for securing access, securing your data, securing all your clouds, defending against threats, and managing risk and privacy. Zero Trust benefits from AI-enabled solutions and provides the agile security required to protect the use of AI technologies. Developing and managing a trust fabric for your organization addresses the need for secure access. It can integrate with and inform each solution in your framework as needed for end-to-end visibility, defense, and optimization.
The core threads of a trust fabric
The first key word is trust. Trustworthiness of human and non-human identities will be determined by real-time evaluation and verification of valid decentralized identity credentials. It isn’t an idea of “trust but verify.” It’s “actively verify, then trust.” And the second key word is fabric. A fabric is a cybersecurity mesh architecture—a composable and scalable approach to extending security controls, even to widely distributed assets.1 With a trust fabric, organizations first evaluate the risk level of any identity or action. Then, they apply a universal Conditional Access engine. It meters secure access with smart policies and decisions informed by governance, compliance, and current global cyberthreats. And it takes into account any important factors or anomalies relevant to the situation at any given moment.
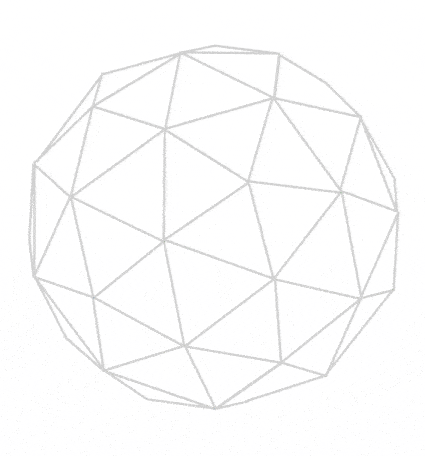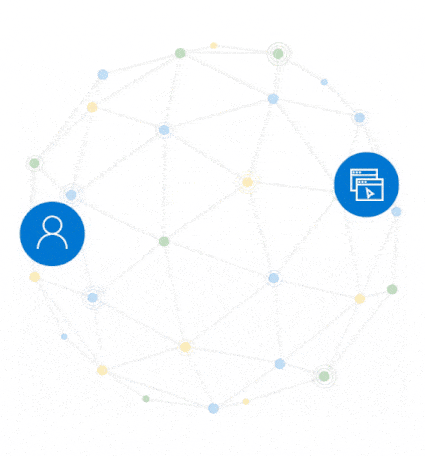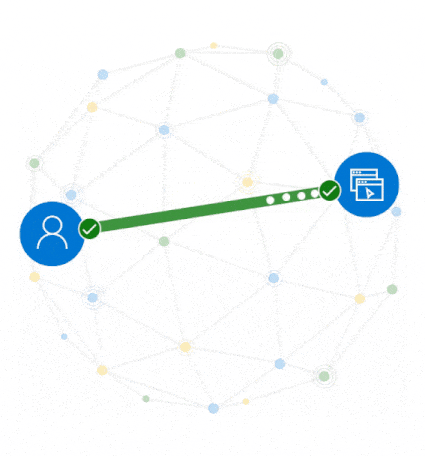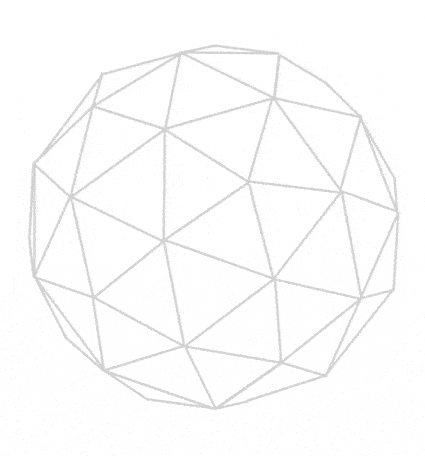
Figure 2. A trust fabric verifies identities, validates access conditions, checks permissions, encrypts the connection channel, and monitors for compromise.
For a trust fabric, the following capabilities and conditions must be continuously evaluated in real-time:
- Verify the initiating identity is trustworthy, secure, and verified, as well as the resource, person, or AI they’re connecting with.
- Protect the communication channel that transports data.
- Ensure access extends no further than needed.
- Sever the connection the moment fraud or risk is detected.
The Microsoft trust fabric
At Microsoft, we continue to design and innovate our identity, endpoint, and network access portfolio to make the trust fabric a reality for our customers, today and tomorrow. Microsoft Entra helps our customers create their trust fabric for the era of AI that securely connects any trustworthy identity with anything, anywhere.

Figure 3. Microsoft Entra is a comprehensive identity and network access solution for securing access for any trustworthy identity to any resource from anywhere.
It’s likely that your organization is already on the journey to create your own trust fabric. To be sure you’ve got the basics covered, we’ve documented the top “quick security wins” in our Microsoft Entra Fundamentals documentation on Microsoft Learn:
- Enable multifactor authentication.
- Identity secure score.
- Improve your security posture.
- Integrating all your apps with Microsoft Entra ID.
- Security defaults.
- Block less secure authentications.
As organizations learn more about trust fabric and continue to apply Zero Trust principles, we’ll be sharing more of our perspective. Keep an eye out for my next blog, focusing on the four stages of trust fabric maturity and how to assess and plan for each stage.

Microsoft Entra
Protect any identity and secure access to any resource with a family of multicloud identity and network access solutions.
Learn more
To learn more about Microsoft Security solutions, visit our website. Bookmark the Security blog to keep up with our expert coverage on security matters. Also, follow us on LinkedIn (Microsoft Security) and X (@MSFTSecurity) for the latest news and updates on cybersecurity.
1Cybersecurity Mesh, Gartner.
The post How implementing a trust fabric strengthens identity and network appeared first on Microsoft Security Blog.
Source: Microsoft Security
